Fluoroquinolones have broad antibacterial spectrum, strong antibacterial activity, low adverse reactions, good tissue permeability, high oral bioavailability, long administration interval and convenient administration. They are commonly used in the treatment of infectious diseases such as respiratory tract infection and urinary tract infection. The structure of fluoroquinolone antibacterial drugs is characterized by the presence of fluorine in the sixth position of the quinolone parent nucleus.
However, in recent 10 years, due to the selective pressure generated by the wide application of this type of drugs, drug-resistant strains increase, especially in recent years, quinolone-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae has cross-resistance, which is resistant to penicillin, macrolide antibiotics and quinolone antibiotics. At the same time, it was found that some fluoroquinolones could cause QTc interval prolongation of electrocardiogram, hepatotoxicity and phototoxicity, which limited their application.
In order to overcome the above shortcomings of fluoroquinolones, it is urgent to develop new structural compounds with good antibacterial activity, broad antibacterial spectrum and as small as possible adverse reactions against multi-drug resistant bacteria. A series of recently developed new fluoroquinolone-free (NFQ) drugs containing 8-methoxyl are different from fluoroquinolone antibiotics in that they do not have fluorine on position 6 of the quinolone parent nucleus, but still have strong in vitro antibacterial activity. nemonoxacin is a new NFQ selective bacterial topoisomerase inhibitor.
Compared with the fluoroquinolones currently on the market, Nenofloxacin represents a new class of structural drugs. nemonocacin (TG-873870), a new quinolone drug developed by Procter & Gamble (P&G), showed significant antibacterial activity against a variety of clinically relevant pathogens, including Staphylococcus aureus and multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae. The results of the experiment in infected mice showed that the antibacterial effect of this product was stronger than most of the current quinolones. In addition, the product has excellent pharmacokinetic properties and is well tolerated.
 Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China.
Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com
amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com +86 (028) 84841969
+86 (028) 84841969 +86 135 5885 5404
+86 135 5885 5404

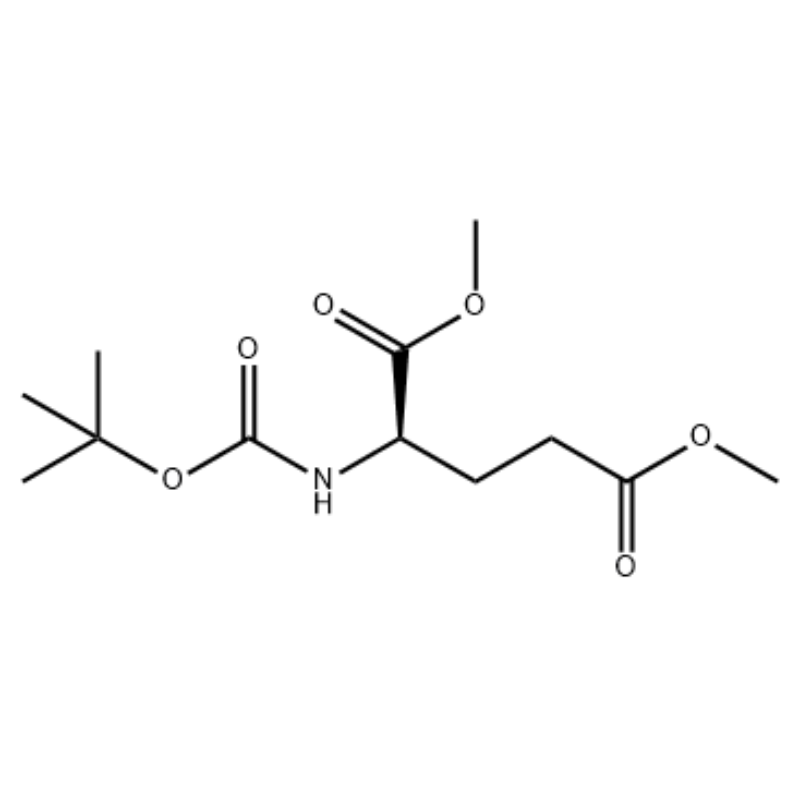
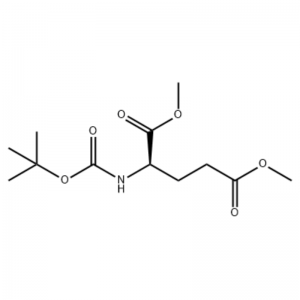



















.png)


