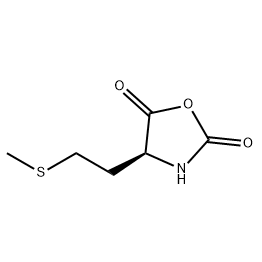
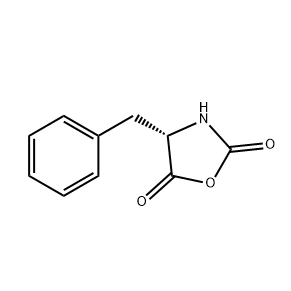
Peptide Synthesis: Met-NCA is highly reactive and can be used as a building block for peptide synthesis. It efficiently reacts with amines to form peptide bonds, enabling the construction of peptides with specific sequences and properties. This method is particularly useful for the synthesis of biologically active peptides that can be used in pharmaceutical research or as therapeutics.
Drug Discovery and Development: Methionine is an essential amino acid that plays crucial roles in biological processes. By incorporating Met-NCA into drug molecules, researchers can introduce methionine residues that may enhance the bioactivity, targeting ability, or stability of the drugs. This approach can lead to the discovery of novel therapeutics with improved pharmacological profiles.
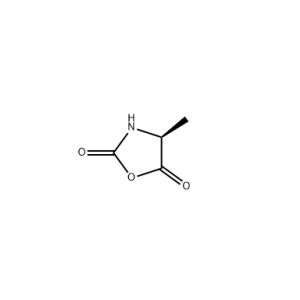
Material Science Applications: Met-NCA can also be used in the synthesis of polymers and materials with methionine-based functionalities. These materials may exhibit unique properties such as biocompatibility, biodegradability, or specific interactions with biological systems. They can be used in tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, or the development of biomaterials for medical applications.
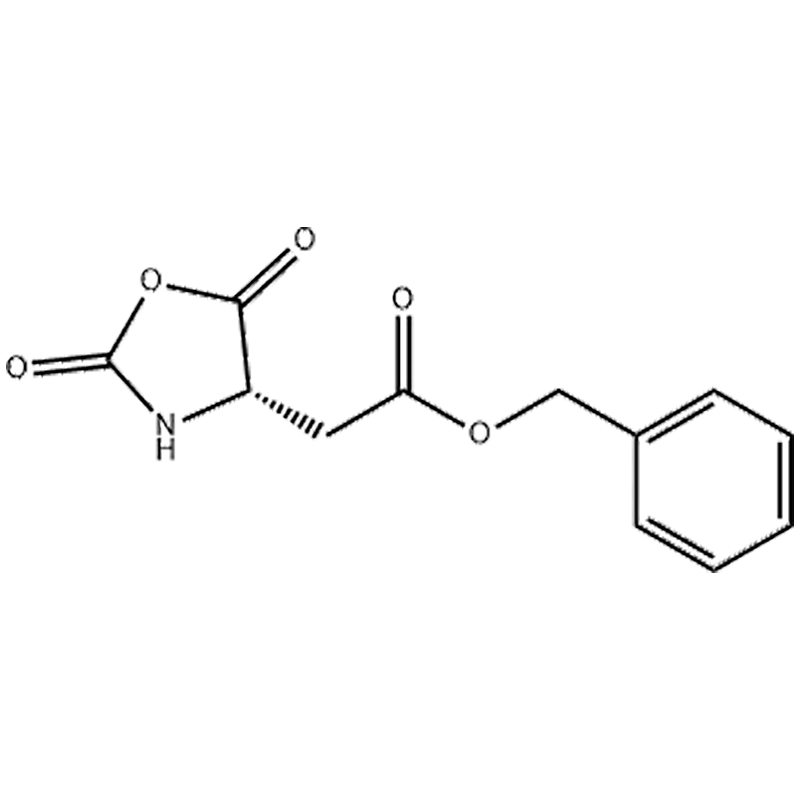
Bioconjugation and Protein Modification: Met-NCA can be used as a reagent for bioconjugation reactions, allowing the attachment of various molecules or functional groups to proteins or peptides. This capability enables the modification of proteins with desired properties, such as improved solubility, stability, or targeting ability. Bioconjugation reactions using Met-NCA can be used in the development of protein-based therapeutics, biosensors, or diagnostic tools.
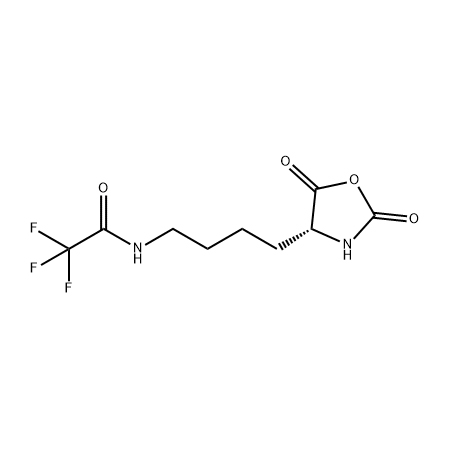
Biochemical and Cellular Studies: The ability to synthesize peptides and proteins containing methionine residues using Met-NCA provides a powerful tool for biochemical and cellular studies. Researchers can use these molecules to investigate protein-protein interactions, enzyme kinetics, or cellular signaling pathways. Met-NCA-derived peptides can also be used as probes or inhibitors to study biological processes and disease mechanisms.
 Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China.
Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com
amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com +86 (028) 84841969
+86 (028) 84841969 +86 135 5885 5404
+86 135 5885 5404
















.png)


