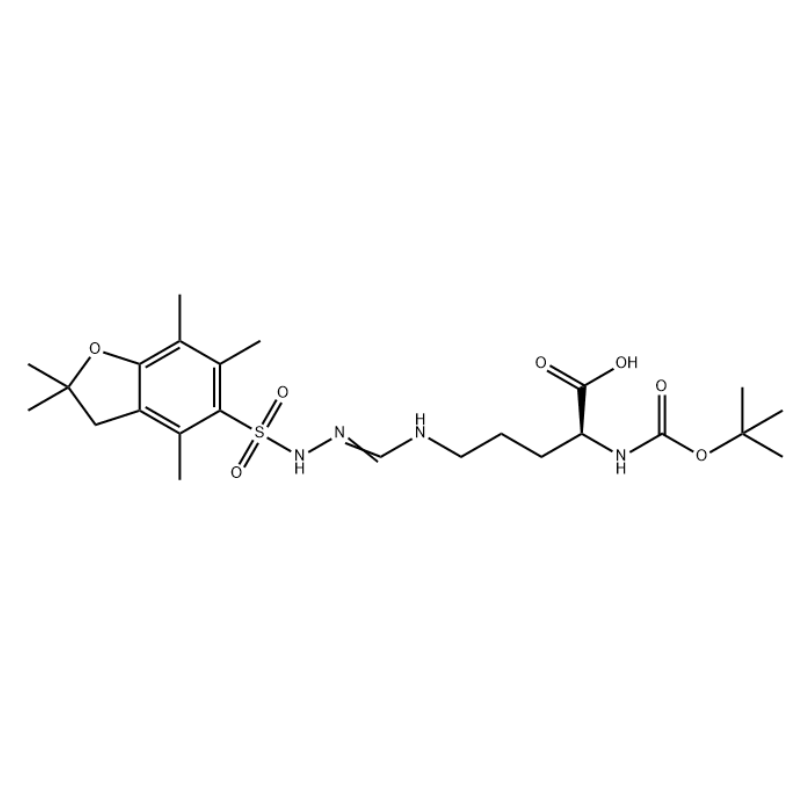
Boc-Arg (Pbf) -OH is an arginine derivative.
Bivalirudine, a synthetic anticoagulant that is a 20-peptide cousin of hirudin, was approved for sale in the United States in 2000. The injection is a white, loose substance or an amorphous solid. Bivarudine can bind specifically to the thrombin catalytic site and the anion external binding site, and directly inhibit the activity of thrombin, thus inhibiting the reaction catalyzed and induced by thrombin, and its effect is reversible. Bivarudine is mainly used as an anticoagulant for elective percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in adults.
Bivarudine is a direct inhibitor of thrombin, which specifically binds to the catalytic sites and anion exo-binding sites of thrombin free and on thrombus. The binding process between bivaludine and thrombin is reversible, and thrombin can restore the original biological activity of thrombin by slowly enzymolysis of the peptide bond between bivaludine Arg3-Pro4.
In vitro studies have shown that bivarudine can not only inhibit the lateral free thrombin, but also inhibit the thrombin binding with blood clots without being neutralized by the substances released by platelets. It can prolong the partial prothrombin time (APTT), thrombin time (TT), prothrombin time (PT) and active coagulation time (ACT) activated by normal plasma. There is a linear relationship with the concentration of bivarudine, but whether this correlation exists in clinical application is unclear.
It has been reported in the literature that the pharmacokinetics of patients undergoing percutaneous coronary angioplasty (PTCA) are linear after intravenous administration of bivarudine. The patient was given 1 mg/kg intravenously as a load dose, followed by another IV infusion of 2.5 mg/kg/hr for 4 hours, which stabilized at 12.3±1.7 mg/ml in vivo. Bivarudine is cleared from plasma by renal hydrolysis and protease degradation. The clearance half-life of patients with normal renal function is about 25min, and the clearance half-life of patients with moderate and severe renal insufficiency is extended. About 25% of bivarudine can be removed by dialysis and cleared by hemodialysis. ACT should be monitored in patients with renal impairment. In healthy volunteers, the anticoagulant effect was immediately observed after intravenous administration of bivarudine, with prolonged PT, ACT and APTT. One to two hours after withdrawal, ACT returned to the pre-administration level.
 Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China.
Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com
amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com +86 (028) 84841969
+86 (028) 84841969 +86 135 5885 5404
+86 135 5885 5404



















.png)


