Card bei oxytocin (Carbetocin) is a kind of synthesis of long-acting with characteristics of agonist oxytocin 8 peptide content, its clinical and pharmacological properties similar to natural produce oxytocin. Like oxytocin, cabetin binds to oxytocin receptors in the smooth muscle of the uterus, causing rhythmic contractions of the uterus, increasing its frequency and increasing uterine tension on top of the original contractions. Levels of oxytocin receptors in the uterus are low during non-pregnancy and increase during pregnancy, peaking at birth. Therefore, cabetin has no effect on the non-pregnant uterus, but has effective uterine contractions on the pregnant uterus and the uterus after birth. Either intravenously or intrintrally, the uterus contracts rapidly, reaching a definite strength within 2 minutes. A single dose of intravenously administered capetin is active in the uterus for approximately one hour, which is sufficient to prevent postpartum bleeding immediately after delivery. The frequency and amplitude of contractions after postpartum administration of carpetine were longer than that of oxytocin. Studies have shown that when given a single dose of 100μg intravenously immediately after a caesarean section under epidural or lumbar anesthesia, carbetin is significantly superior to placebo in preventing uterine hypotonia and reducing postpartum bleeding. Carpetine given in the early postpartum period may also promote uterine recovery.
Cabetin binds to oxytocin receptors in the smooth muscle of the uterus to cause the uterus to contract rhythmically, increasing its frequency of contraction and increasing uterine tension. A single dose of carbetin can be given immediately after the delivery of the fetus to prevent postpartum bleeding. It has been found that postpartum intravenous injection of oxytocin combined with the administration of cabetin can effectively prevent postpartum blood loss. After cesarean section, the use of cabetin combined with oxytocin can strengthen uterine contraction, reduce the amount of blood loss after cesarean section, the effect is even better than hemabate. For women with cicatritic uterus, placenta previa and other high risk factors for postpartum hemorrhage, carbetin can effectively prevent the occurrence of postpartum hemorrhage. It is used for elective epidural or lumbar anesthesia after cesarean section to prevent uterine contraction weakness and postpartum hemorrhage.
 Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China.
Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com
amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com +86 (028) 84841969
+86 (028) 84841969 +86 135 5885 5404
+86 135 5885 5404

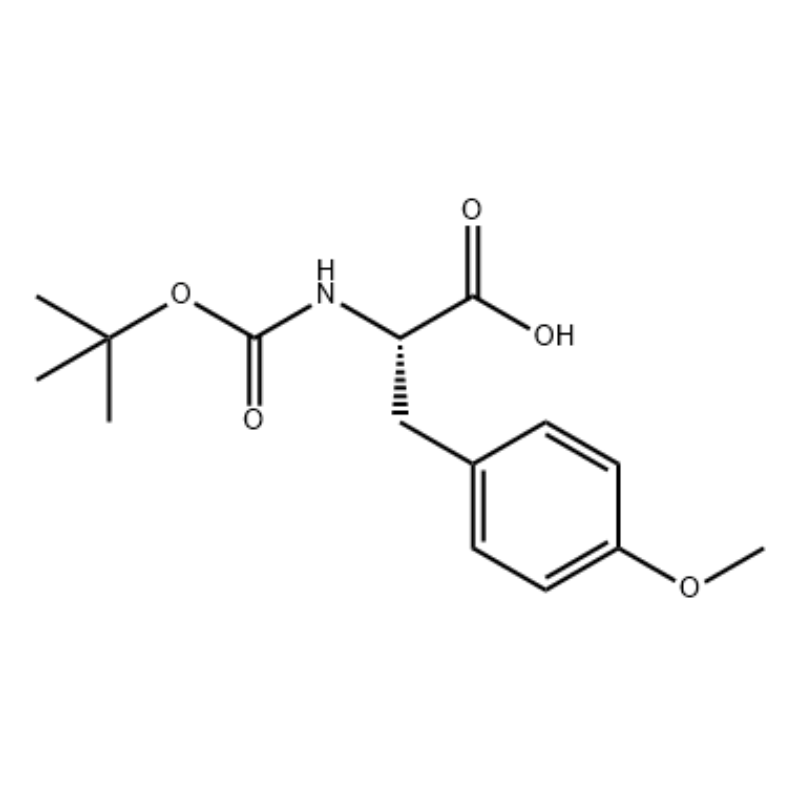
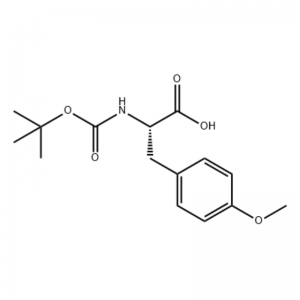









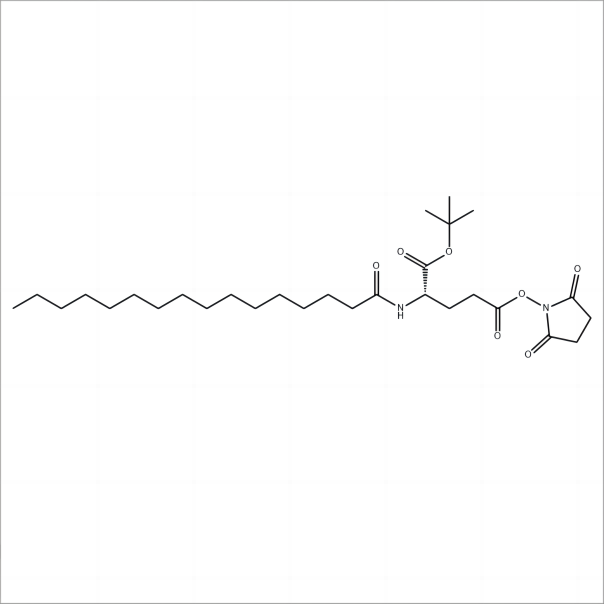









.png)


