Cabetin injection, cabetin is used after elective epidural or lumbar anesthesia caesarean section to prevent uterine contraction weakness and postpartum bleeding. The use of capectin has not been studied for emergency caesarean section, classical caesarean section, epidural or other caesarean section under anesthesia, or in cases where the woman has a history of heart disease, hypertension, known clotting disease, or liver, kidney, and endocrine diseases (excluding gestational diabetes). Treatment with capetin after vaginal delivery has also not been properly studied and the dose has not been determined.
Carbetin is used after elective epidural or lumbar anesthesia caesarean section to prevent uterine contraction weakness and postpartum bleeding.
The use of capectin has not been studied for emergency caesarean section, classical caesarean section, epidural or other caesarean section under anesthesia, or in cases where the woman has a history of heart disease, hypertension, known clotting disease, or liver, kidney, and endocrine diseases (excluding gestational diabetes). Treatment with capetin after vaginal delivery has also not been properly studied and the dose has not been determined.
A single dose of 100 micrograms (1 ml) of capetin is given intravenously and only slowly in a single dose of 1 minute after the baby has been delivered by caesarean section under epidural or lumbar anesthesia. Cabetin can be given before or after delivery of the placenta, or as directed by a doctor.
Compared to oxytocin, the effects of cabetin are prolonged, and the resulting uterine contractions cannot be stopped simply by discontinuing the drug. Therefore, carpetine should not be given before delivery for any reason, including selective or drug-induced production. Inappropriate use of capetin during pregnancy could theoretically produce symptoms similar to those of oxytocin overdose, These include strong (hypertonic) and persistent (tonic) contractions following uterine hyperstimulation, disturbances during labor, uterine rupture, cervix and vaginal tears, postpartum hemorrhage, decreased utero-placental blood perfusion and various fetal heart slowdowns, fetal oxygen deficiency, hypercapnia, and even death.
Capetin should not be used in patients who are allergic to oxytocin and capetin.
Carbetin should not be used in patients with vascular disease, especially coronary artery disease, but should be used with extreme caution.
Capetin is also not to be used in children.
 Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China.
Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com
amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com +86 (028) 84841969
+86 (028) 84841969 +86 135 5885 5404
+86 135 5885 5404

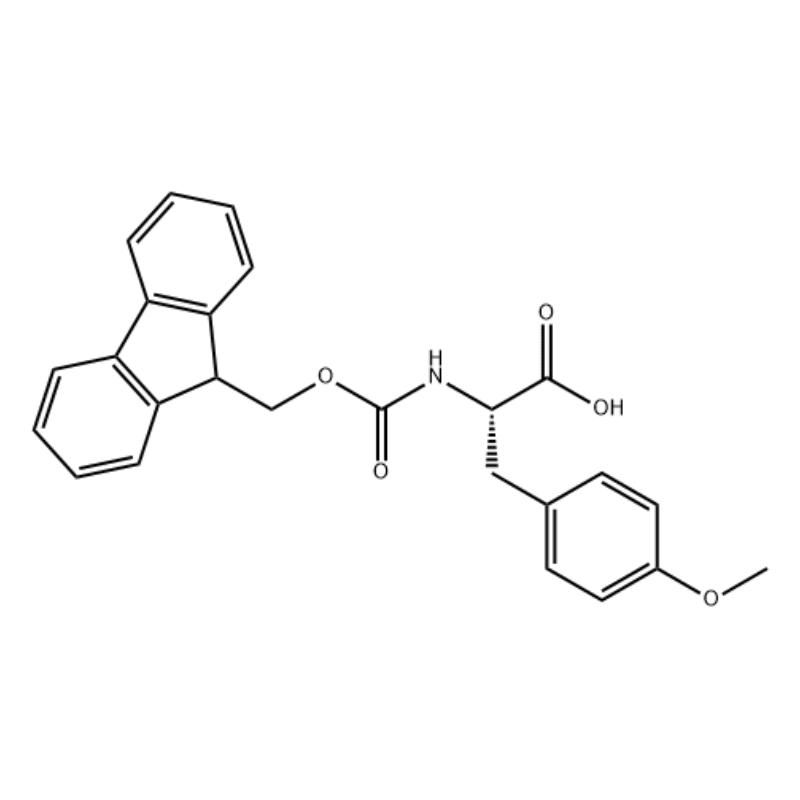
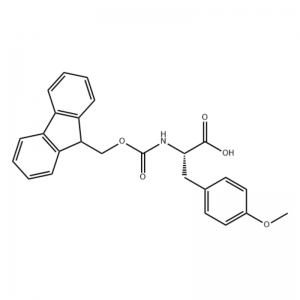



















.png)


