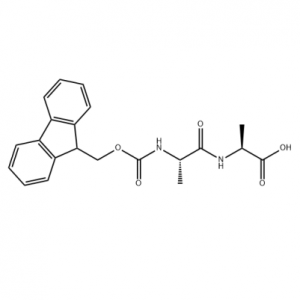
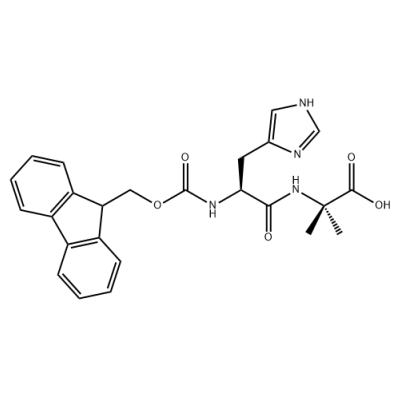
87512-31-0 Fmoc-L-Ala-Ala-OH can be one of intermediates of Thymalfasin.
Thymalfasin is currently mainly used for the treatment or adjuvant therapy of various liver diseases, including hepatitis B, hepatitis C, cirrhosis, primary liver cancer, and viral fulminant hepatitis. The side effects of thymalfasin treatment are low, and patients tolerate it well. Additionally, thymalfasin is included in the national medical insurance category B for the treatment of hepatitis B and hepatitis C, reducing the financial burden for patients.
Thymalfasin is widely used in the treatment of tumors due to its ability to significantly reduce the recurrence rate after surgery and the side effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
Thymalfasin can also be used to treat malignant tumors such as pancreatic cancer, lung cancer, and metastatic brain tumors, as well as autoimmune diseases like rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, and other immune-related diseases such as leukemia. After treatment, the recurrence rate after surgery is significantly reduced, and the side effects of radiotherapy and chemotherapy are reduced.
Radiotherapy is a commonly used treatment for esophageal cancer, nasopharyngeal cancer, cervical cancer, and advanced lung cancer. However, radiotherapy can also cause immune dysfunction in the body. The combined use of thymalfasin can extend the interval between chemotherapy sessions and has clinical significance in improving patient survival rates.
Chemotherapy combined with thymalfasin can become a new treatment option for patients with advanced tumors. The combination of thymalfasin with chemotherapy for malignant lymphomas, gastric cardia cancer, gastric cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, rectal cancer, and other malignancies can improve patients' cellular immune function and reduce adverse reactions.
Thymalfasin can also be used in combination with other drugs for anti-infective treatment. Compared with conventional anti-infective treatment, the combination of thymalfasin and antibiotics in the treatment of recurrent respiratory infections in children has reduced the frequency of respiratory infections, shortened the duration of antibiotic use, and significantly improved the effectiveness rate. Thymalfasin also has a high auxiliary and synergistic effect on the treatment of refractory pulmonary tuberculosis. Adding thymalfasin to the treatment of herpes zoster is effective, and it is superior to conventional treatment methods in terms of the duration of herpes cessation, wound healing, and pain relief. Using thymalfasin in conjunction with influenza vaccination can improve the immune resistance of the elderly against diseases and reduce respiratory illnesses, with the effect being more pronounced in older individuals.
Finally, thymalfasin can also be used to treat condyloma acuminata. The recurrence rate in the group treated with laser therapy combined with thymalfasin is lower than that in the conventional laser group, and it shortens the treatment time, thereby reducing the patient's discomfort.
 Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China.
Building 12, No.309, South 2nd Road, Economic Development Zone, Longquanyi District, Chengdu, Sichuan, China. amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com
amy@enlaibio.com / cynthia@enlaibio.com / edison@enlaibio.com / daisy@enlaibio.com +86 (028) 84841969
+86 (028) 84841969 +86 135 5885 5404
+86 135 5885 5404












![1118767-15-9 Fmoc-L-Lys[OctotBu)-Glu-(otBu)-AEEA-AEEA]-OSu](https://cdn.globalso.com/jylpharm/1118767-15-9.png)




.png)


